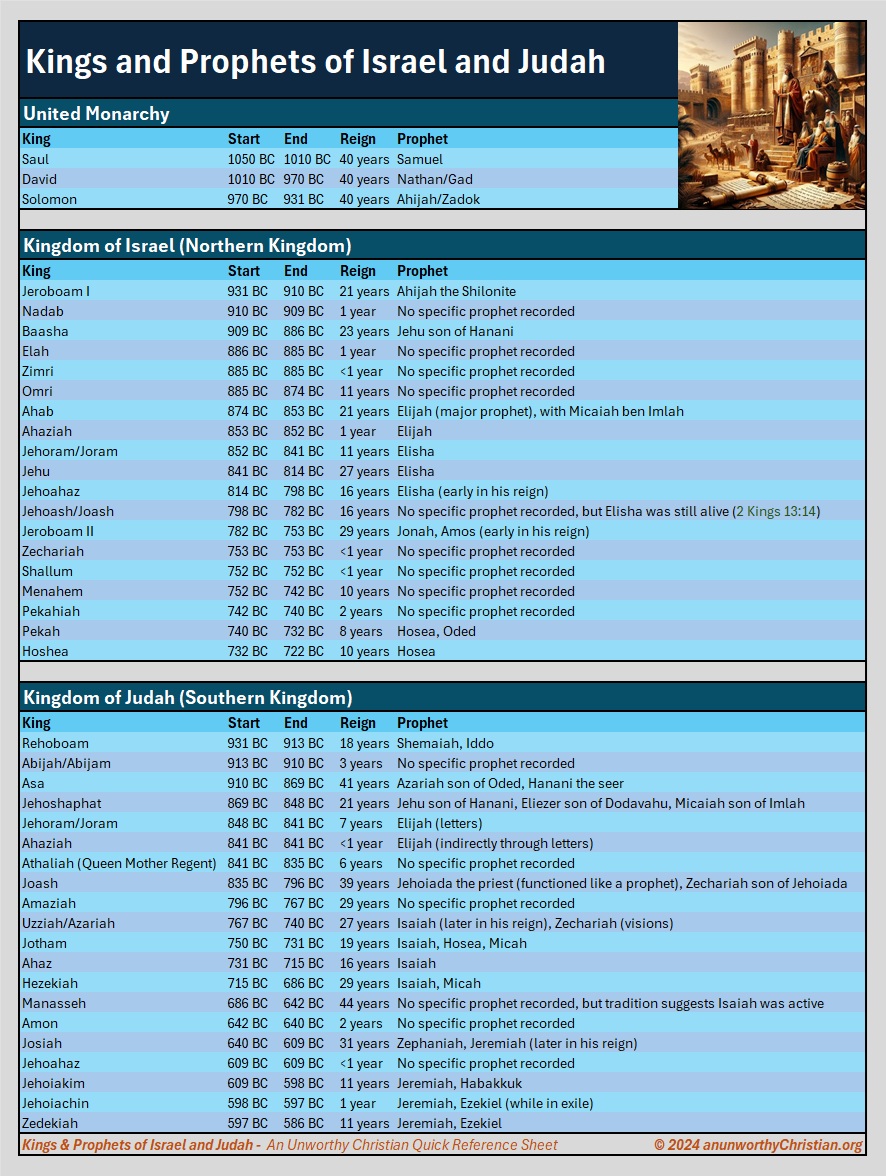
Kings and Prophets of Israel and Judah
A Chart of all Kings and Prophets from the Old Testament
The Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah are significant entities in the Old Testament, each with its own unique history, geographical location, and destiny. Their emergence and distinction are rooted in the complex socio-political and religious developments of ancient Israelite society.
Initially, the Israelites formed a united monarchy under the leadership of King Saul, followed by David and then Solomon. This united kingdom, often referred to simply as Israel, was characterized by significant expansion and prosperity, especially under King David and his son Solomon. The capital was established in Jerusalem under David, and Solomon is credited with building the First Temple there, a central place of worship for the Israelites.
However, after Solomon's reign, the united monarchy experienced internal conflict and external pressures that led to its division into two separate kingdoms around 930BC. This division was partly due to Solomon's policies, which included heavy taxation and forced labor to support his ambitious building projects, including the Temple in Jerusalem. Upon Solomon's death, his son Rehoboam ascended to the throne. Rehoboam's harsh stance towards the northern tribes led to the fracturing of the united kingdom.
Kingdom of Israel (Northern Kingdom)
-Consisted of ten of the twelve Israelite tribes (excluding Judah and Benjamin)
-The capital was initially established in Shechem, but later moved to Tirzah and eventually to Samaria under King Omri, which became the most significant and enduring capital
-The Kingdom of Israel lasted from around 930BC until 722BC, when it fell to the Assyrian Empire. The Assyrians deported many Israelites, leading to the "Lost Tribes of Israel"
-The religious practices in the Kingdom of Israel were diverse and often included the worship of Canaanite gods alongside YHWH. This syncretism was criticized by prophets like Elijah and Elisha, who advocated for the exclusive worship of YHWH
Kingdom of Judah (Southern Kingdom)
-Comprised primarily of the tribes of Judah and Benjamin
-Jerusalem was the capital, which housed the Temple, the central place of worship built by Solomon. The Temple and Davidic lineage in Jerusalem gave Judah a significant religious status
-The Kingdom of Judah lasted longer than the northern kingdom, surviving until 586BC when it fell to the Babylonian Empire. The Babylonians destroyed the Temple and deported many Judeans to Babylon, an event known as the Babylonian Exile
-Despite its smaller size and less fertile land, Judah maintained a stronger sense of unity and identity, partly due to the centralizing religious practices centered around the Temple in Jerusalem
The prophets of the Old Testament played significant roles in both kingdoms, often calling for repentance, social justice, and a return to the worship of YHWH alone. The division of the united kingdom into Israel and Judah and their subsequent fates are pivotal themes in the Old Testament, reflecting the complexities of faith, identity, and power in ancient Israelite society.
Kings and Prophets Chart
Click the below chart to view in detail